- The ISP provides the IP Addresses → 4 byte (4 * 8 bits = 32 bits) address
- Static IP → IP Address does not change (e.g. for web services)
- Dynamic IP → IP addresses change frequently (e.g. phone, laptop and personal devices)
- Private IP → Valid only within a local network (unique within the network)
- Public IP → Accessible anywhere on the internet (assigned to router)
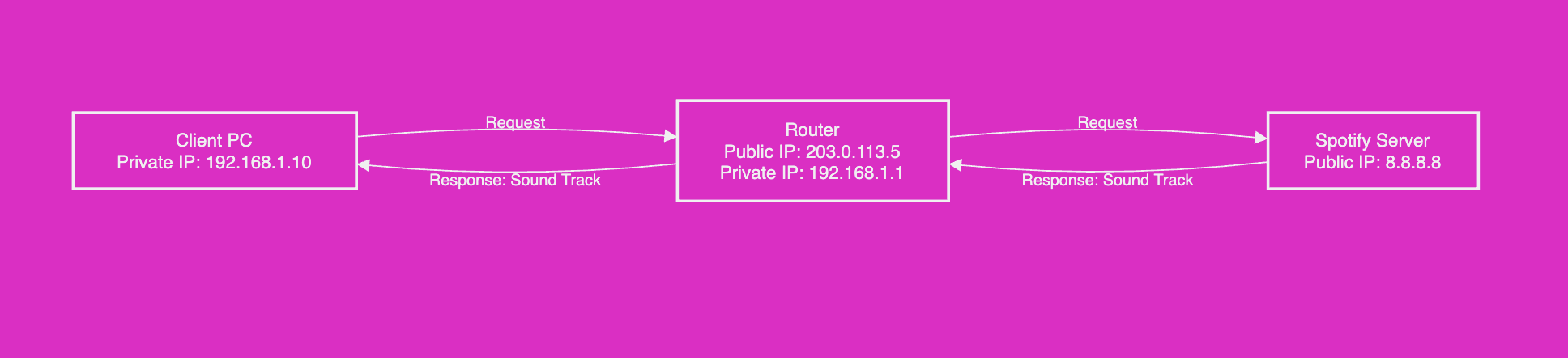
- Format: XX.XX.XX.XX
- Hierarchy → First byte corresponds to the larger network, then the following is more and more specific
- IPv6 → Expanding to 6bytes instead of only 4 bytes (but lacking infrastructure)
